5 Measurement principle
The method for detecting airborne particles is based primarily on the particle diameter. Due to the low
scattered light intensity of ultra-fine particles, the optical detection of particles with a diameter of less
than approximately 200 nm stops. To cover the widest possible range of particle diameters, here
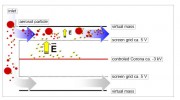
ranging from 10 nm to 35μm, the GRIMM MINI-WRAS 1371 combines two measurement methods: the
electrical detection of ultrafine particles by means of a Faraday cup electrometer in the so-called
Nano-Sizer and the optical detection of particles with diameters greater than approximately 200 nm by
measuring the scattered light intensity. The sample air is first passed through the optical aerosol
spectrometer. Then the particles with a diameter greater than about 2 2µm are separated in order to
keep the contamination of the subsequent electric sensor as small as possible. The combination of the
two measurement methods results in a particle size distribution in the range of 10 nm to 35μm in a
total of 41 size classes.
5.1 Measurement principle of the optical aerosol spectrometer
The sample air is conducted into the measuring chamber directly from the aerosol intake or through
the application-specific sample air collector. Particles contained in the sample air are captured in the
measuring chamber using light-scattering photometry. The scattered light impulse of each individual
particle is counted and the intensity of the scattered light signal is assigned to a particle size. The
measurement principle is shown schematically in Figure 4-1.
With the 1371-MINI-WRAS, the wavelength is in the visible range of 660 nm. The laser diode can be
operated in what is known as multiplex mode, which means that the intensity of the laser beam is
modulated. This allows particles to be detected in a very broad size range from 0.25 µm to 32 µm with
this model. The laser beam is focused into a flat band by lighting optics. In focus the laser beam
evenly lights a small sensing volume and is then conducted into a light trap.
The sample air is aerodynamically focused and conducted through the interior of the sensing volume
as a particle stream.